
Vulnerability Management Lifecycle: Your 5-Step Guide to a Secure System
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) adds more than 2,000 new security vulnerabilities every month to the National Vulnerability Database.
While security teams can’t tackle every vulnerability, they need a systematic approach to pinpoint and address those posing the greatest risk.
That’s where the vulnerability management lifecycle proves indispensable.
In this blog post, we’ll take you through each stage of the vulnerability management lifecycle, from initial planning to ongoing monitoring. We’ll also explore some of the common challenges organizations face.
Vulnerability Management Lifecycle: A 5-Step Process
In this section, we will discuss the 5 steps of vulnerability management lifecycle. We will also take an example of an eCommerce website to understand it better.
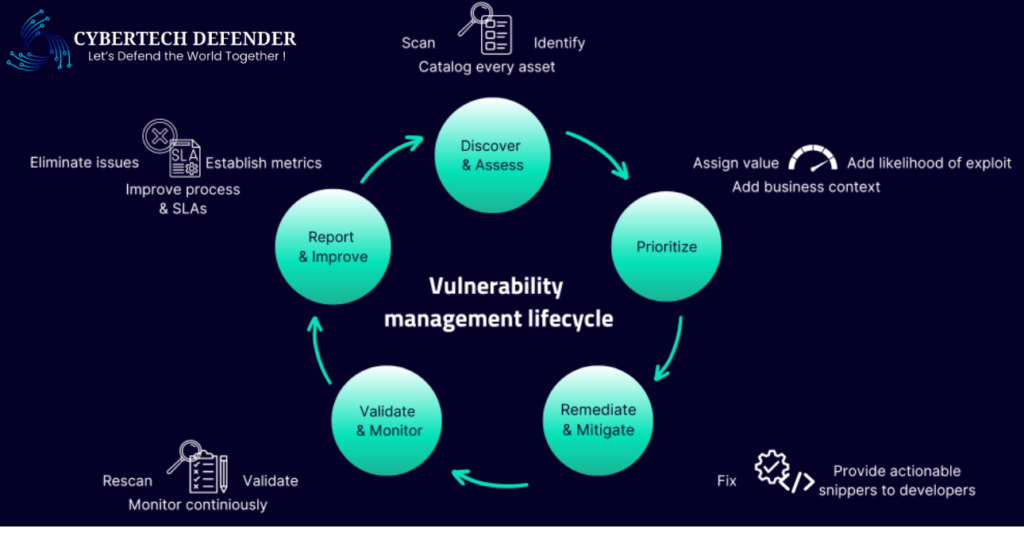
1. Planning
As with any endeavor, this also starts with planning. The organization defines the scope, sets clear goals, and identifies the resources and tools it will use.
For example, a retail company might decide that its eCommerce website and customer database are most importance. So it may focus its vulnerability management efforts on them. It may allocate a dedicated team and a budget for training and tools.
2. Identification
In this stage, organizations identify and document all IT assets, like servers and systems, connected to the network. They also conduct vulnerability scans to identify any weaknesses.
In our example, the team will take into account all the servers and devices connected with the eCommerce platform. It will also run a vulnerability scan to identify any known weaknesses in the system like outdated software or misconfigurations.
3. Analysis
After the identification of assets and risks, the organization analyzes vulnerabilities based on severity and potential impact. Then it prioritizes them based on
- How easily hackers can exploit them
- Value of the assets they could affect
In our example, the cybersecurity team discovers a critical vulnerability in a widely used web server software that could allow remote code execution. They analyze the potential impact of this vulnerability, considering the sensitivity of customer data stored on the e-commerce platform. Given the high severity and potential for exploitation, they prioritize this vulnerability for immediate remediation.
4. Remediation
After creating the priority list, it is time to take action. This stage focuses on fixing the issues found in the “Analysis” stage. This may involve
- applying patches
- reconfiguring systems
- replacing outdated hardware or software
In our example, this step will include the company promptly applying a security patch released by the web server software vendor to address the critical vulnerability. They will also implement additional security measures, such as web application firewalls, to further protect their eCommerce platform.
5. Continuous Monitoring
Even after fixing the vulnerabilities, the work is still not done. Cybersecurity is an ongoing process. The organization needs to maintain constant vigilance, regularly scan for new vulnerabilities, and ensure that existing fixes remain effective. Staying up-to-date on the latest security threats and adapting defenses accordingly is also crucial.
Continuing with our example, the security team will establish a process for regular vulnerability scans and penetration testing to proactively identify and address new weaknesses. They might also subscribe to threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about the latest attack techniques and adjust their security controls accordingly.
7 Challenges with the Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
With AI hacking on the rise, the threat of cyberattacks is always looming. Although the vulnerability management lifecycle is essential for strengthening cybersecurity defenses, it is not without its challenges.

Increase in Attack Surface
As the scope of technology increases, so will the attack points of hackers. People and businesses are using technologies like IoT, cloud computing, mobile devices, etc., which is giving attackers more places to attack. This increases the difficulty in evaluating the list of IT assets.
Overwhelming Volume of Vulnerabilities
Tools like vulnerability scanners can generate massive amounts of data and flag thousands of vulnerabilities. For security teams, it is sometimes too difficult to digest this information, classify the most important ones, and then provide remediation in a timely manner.
Lack of Resources and Expertise
This is another area of concern for a majority of the organizations. Many of them lack qualified cybersecurity professionals which makes it difficult for them to implement a robust vulnerability management program. The shortage of such professionals further makes the situation worse.
Balancing Security and Business Needs
Installing security patches can sometimes disrupt business operations or mess with how systems work. This can be a real headache for some companies because it involves coordinating with various teams, both within the company (like IT) and outside (like the people who made the software).
Keeping Up With Changing Trends
New vulnerabilities are discovered every day, the trends in cybersecurity keep changing, and cybercriminals are constantly developing new attack methods. Keeping pace with these changes and ensuring that security controls are up-to-date can be a daunting task.
Third-Party Risk
Organizations often rely on third-party vendors and suppliers, introducing potential vulnerabilities into their supply chain. Managing and mitigating third-party risks requires effective communication, due diligence, and ongoing monitoring.
Lack of Automation
Despite advances in technology, organizations still rely on inefficient manual processes like vulnerability detection, risk analysis, and remediation which are time-consuming and error-prone. Automating these tasks can improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error, but implementing and maintaining automation tools can be challenging.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of strategic planning, investment in the right tools and technologies, and a commitment to ongoing training and development for cybersecurity professionals.
By addressing these hurdles, organizations can build a more resilient security posture and effectively protect their critical assets from cyber threats.
Master Vulnerability Management with CyberTech Defender
As you’ve seen, the vulnerability management lifecycle is a continuous process, demanding constant vigilance and adaptation in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats. The challenges are real, from the sheer volume of vulnerabilities to balancing security with business needs.
But don’t let these challenges discourage you. By understanding the lifecycle and taking proactive steps to address potential weaknesses, you can significantly bolster your defenses and reduce the risk of a cyberattack.
If you’re ready to equip yourself with the knowledge and skills to master the vulnerability management lifecycle, consider enrolling in the Vulnerability Management course offered by CyberTech Defender.
Don’t wait for a breach to expose your vulnerabilities. Take control of your cybersecurity future today with CyberTech Defender!



